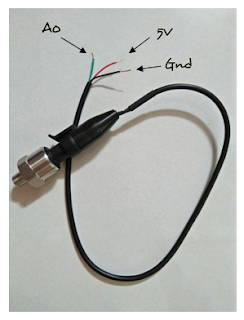
WATER PUMP PRESSURE
23/2/18
I have problem with my pipe. The pipe that i bought is not suitable for my pump. So i have to buy a new one, after that i can test the pump and also the functionality of my pressure sensor. If the pressure sensor show the reading, that means it is working.
I will update more after I buy a new pipe.. ☺
24/2/18
I had go to Jalan Pasar, to buy a battery of 12V as my power supply. And also go to Wangsa Maju to buy a new pipe.
Pipe
12V Battery
After come back home, I connect the supply of 12V to the pump, but it is not functioning. The pipe match well with my pump.
It is not working, there must be something wrong with my power supply, or maybe my pump. I will
find other way to make it function. Stay tuned.. ☺
26/2/18
I'm planning to go to Jalan Pasar yesterday, but it is Sunday. So all shop must be close. So i go to Jalan Pasar on Monday. I buy a new switching power supply power adapter led. Its support 12V and 8.5Amp. My pump should be functioning. And I buy a 3-pin plug to give a supply to the power adapter.
Switching Power Supply Power Adapter Led
3-Pin Plug
I connect all the thing I buy, and test it with my pump. Alhamdulillah, it working very well... ☺
VIDEO
2ND FINAL YEAR PROJECT BRIEFING
The second briefing was conducted at TTL 1 and the attendance is compulsory. The briefing was conducted by Dr. Fadi M. Albatsh.
Date : 28 Feb 2018
Vanue : TTL 1
Time : 3.00 pm - 5.00 pm
This briefing is about result & discussion (chapter 4) and conclusion (chapter 5) in thesis writing. Consist all the matter below:
Result
Result
- Collect all available result.
- Result should answer objective.
- Identify who is our customer, to convince them.
- Try to explain as a future work.
Discussion
- Explain the meaning of the result.
- Do they give new insight?
- Explain in a simple way, so that easier to understand.
Conclusion
- Summarized proposed solution and why it is interesting.
- Summarize weakness and limitation.
- Should related to research question.
- Do not repeat abstract.
That is all the briefing about. Thank you.